Understanding the Five Pillars of Aviation Safety
Aviation safety is the cornerstone of the global aviation industry. With millions of passengers flying daily, ensuring safety is not just a priority but a necessity. The aviation industry has developed a robust framework to maintain and enhance safety standards, often referred to as the Five Pillars of Aviation Safety. These pillars form the foundation of safety management systems (SMS) and are critical to minimizing risks, preventing accidents, and fostering a culture of safety. In this article, we’ll explore these five pillars in detail, their significance, and how they work together to create a safer aviation environment.
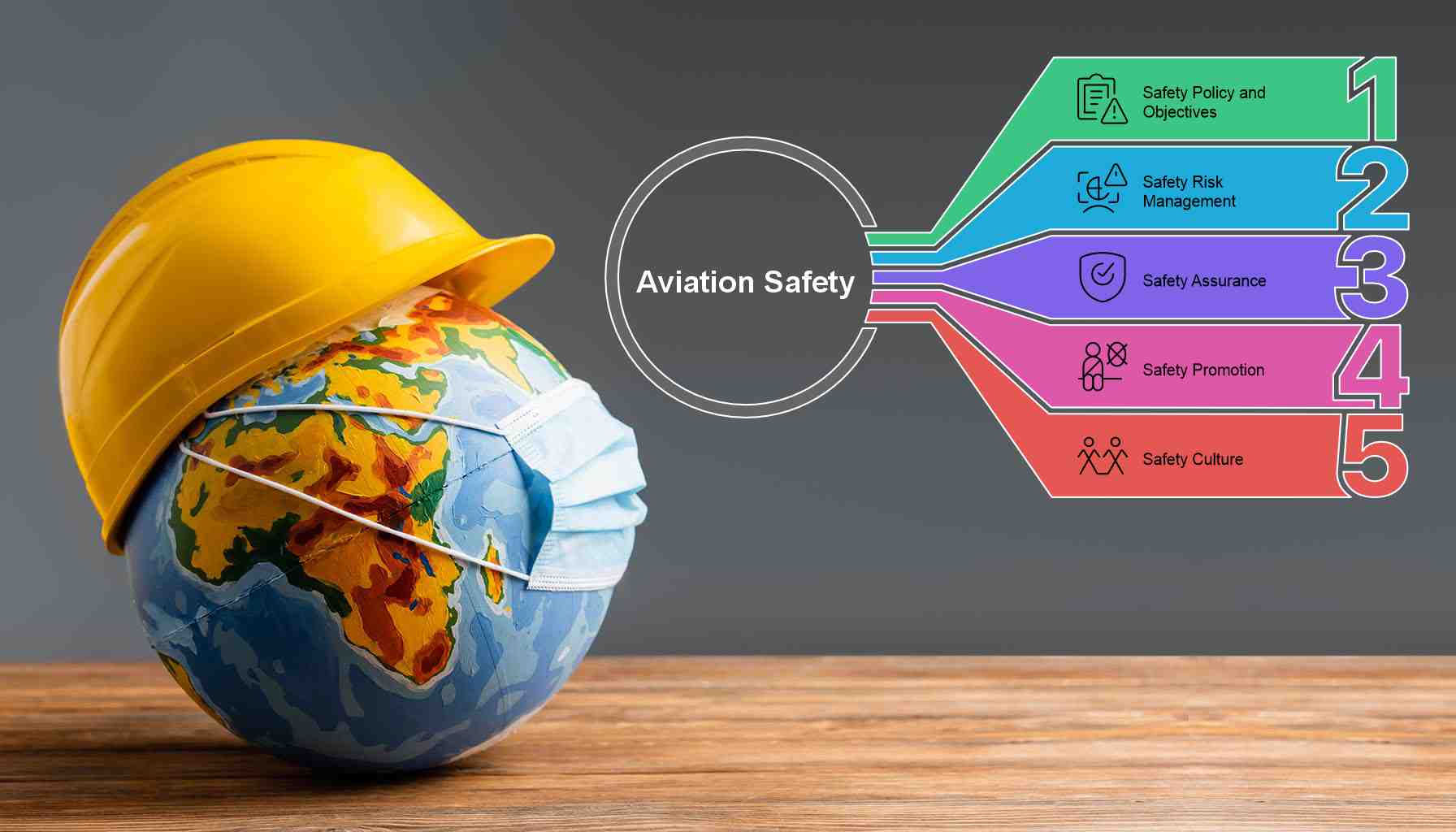
- Safety Policy and Objectives
The first pillar of aviation safety is Safety Policy and Objectives. This pillar establishes the foundation for a safety management system by defining an organization’s commitment to safety. It outlines the principles, goals, and responsibilities that guide safety practices.
- Safety Policy: A clear and concise statement from top management that emphasizes the importance of safety. It communicates the organization’s commitment to maintaining high safety standards and complying with regulatory requirements.
- Safety Objectives: Specific, measurable goals that align with the safety policy. These objectives help organizations track progress and ensure continuous improvement in safety performance.
For example, an airline might set an objective to reduce runway incursions by 20% within a year. This objective would be supported by training programs, improved communication protocols, and enhanced monitoring systems.
Why It Matters: A well-defined safety policy and clear objectives create a unified direction for all employees. It ensures that everyone, from pilots to ground staff, understands their role in maintaining safety.
- Safety Risk Management
The second pillar, Safety Risk Management (SRM), focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. This proactive approach helps prevent accidents before they occur.
- Hazard Identification: The process of recognizing potential hazards, such as adverse weather conditions, mechanical failures, or human errors.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and severity of each identified hazard. This step helps prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing measures to reduce or eliminate risks. This could include updating procedures, enhancing training, or investing in new technology.
For instance, if an airline identifies fatigue among crew members as a risk, it might implement stricter rest requirements and introduce fatigue management programs.
Why It Matters: Safety Risk Management ensures that potential threats are addressed systematically, reducing the likelihood of accidents and enhancing overall safety.
- Safety Assurance
The third pillar, Safety Assurance, involves monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of safety measures. It ensures that the safety management system is functioning as intended and identifies areas for improvement.
- Safety Audits: Regular inspections and evaluations of operations, procedures, and equipment to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Data Analysis: Collecting and analyzing safety-related data, such as incident reports, flight data, and maintenance records. This helps identify trends and emerging risks.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking key safety indicators to measure progress toward safety objectives.
For example, an airline might analyze flight data to identify patterns of unstable approaches and implement corrective actions, such as additional pilot training.
Why It Matters: Safety Assurance provides a feedback loop that ensures continuous improvement. It helps organizations stay proactive and responsive to changing conditions.
- Safety Promotion
The fourth pillar, Safety Promotion, focuses on fostering a positive safety culture within the organization. It involves training, communication, and engagement to ensure that safety is a shared value among all employees.
- Training and Education: Providing employees with the knowledge and skills they need to perform their duties safely. This includes initial training, recurrent training, and specialized courses.
- Communication: Keeping employees informed about safety policies, procedures, and updates. Effective communication ensures that everyone is on the same page.
- Engagement: Encouraging employees to actively participate in safety initiatives. This could include reporting hazards, suggesting improvements, or participating in safety committees.
For instance, an airline might launch a safety campaign to encourage pilots and cabin crew to report near-miss incidents without fear of reprisal.
Why It Matters: A strong safety culture is essential for the success of any safety management system. When employees are engaged and committed to safety, the entire organization benefits.
- Safety Culture
The fifth and final pillar is Safety Culture, which represents the attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors related to safety within an organization. A positive safety culture is characterized by trust, transparency, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
- Leadership Commitment: Leaders must demonstrate a genuine commitment to safety through their actions and decisions. This sets the tone for the entire organization.
- Employee Involvement: Employees at all levels should feel empowered to contribute to safety. This includes reporting hazards, participating in safety programs, and sharing ideas for improvement.
- Learning Environment: Organizations should encourage a culture of learning where mistakes are viewed as opportunities for improvement rather than reasons for punishment.
For example, an airline with a strong safety culture might celebrate employees who identify potential risks, reinforcing the importance of vigilance and proactive behavior.
Why It Matters: Safety culture is the glue that holds the other pillars together. Without a positive safety culture, even the best policies and procedures may fall short.
How the Five Pillars Work Together
The Five Pillars of Aviation Safety are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. For example:
- A strong Safety Policy provides the foundation for Safety Risk Management by defining the organization’s commitment to identifying and mitigating risks.
- Safety Assurance ensures that the measures implemented through Safety Risk Management are effective and identifies areas for improvement.
- Safety Promotion and Safety Culture work hand in hand to create an environment where safety is prioritized and employees are engaged in safety initiatives.
Together, these pillars create a comprehensive framework that enables organizations to manage safety proactively and effectively.
The Importance of the Five Pillars in Modern Aviation
In today’s fast-paced aviation industry, the Five Pillars of Aviation Safety are more important than ever. With increasing air traffic, evolving technology, and new challenges such as cybersecurity threats, a robust safety management system is essential.
- Global Standards: The Five Pillars align with international standards set by organizations such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). This ensures consistency and interoperability across the industry.
- Public Confidence: Passengers trust airlines to prioritize their safety. By adhering to the Five Pillars, airlines can build and maintain this trust.
- Operational Efficiency: A strong safety management system not only reduces the risk of accidents but also improves operational efficiency by minimizing disruptions and delays.
Conclusion
The Five Pillars of Aviation Safety—Safety Policy and Objectives, Safety Risk Management, Safety Assurance, Safety Promotion, and Safety Culture—form the backbone of modern aviation safety. By understanding and implementing these pillars, aviation organizations can create a safer, more efficient, and more reliable industry. Whether you’re a pilot, an air traffic controller, or a ground crew member, these principles are essential to your role in keeping the skies safe.
As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the Five Pillars will remain a critical framework for managing safety in an increasingly complex and dynamic environment. By embracing these principles, we can ensure that aviation remains one of the safest modes of transportation in the world.